区块链论文速读B会-DSN 2024(1/2)区块链如何容忍对手控制超过一半的系统节点?

Conference:The 54th Annual IEEE/IFIP International Conference on Dependable Systems and Networks
Conference time:2024
1、Byzantine Attacks Exploiting Penalties in Ethereum PoS
利用以太坊 PoS 中的惩罚机制进行拜占庭攻击

Ethereum, Inactivity Leak, Safety, Liveness, Blockchain
以太坊、消极惩罚、安全性、活跃度、区块链
In May 2023, the Ethereum blockchain experienced its first inactivity leak, a mechanism designed to reinstate chain finalization amid persistent network disruptions. This mechanism aims to reduce the voting power of validators who are unreachable within the network, reallocating this power to active validators. This paper investigates the implications of the inactivity leak on safety within the Ethereum blockchain. Our theoretical analysis reveals scenarios where actions by Byzantine validators expedite the finalization of two conflicting branches, and instances where Byzantine validators reach a voting power exceeding the critical safety threshold of one-third. Additionally, we revisit the probabilistic bouncing attack, illustrating how the inactivity leak can result in a probabilistic breach of safety, potentially allowing Byzantine validators to exceed the one-third safety threshold. Our findings uncover how penalizing inactive nodes can compromise blockchain properties, particularly in the presence of Byzantine validators capable of coordinating actions.
2023 年 5 月,以太坊区块链经历了第一次消极惩罚,这是一种旨在在持续的网络中断期间恢复链最终确定的机制。该机制旨在减少网络中无法联系的验证者的投票权,并将这种权力重新分配给活跃的验证者。本文探讨了消极惩罚对以太坊区块链内安全性的影响。我们的理论分析揭示了拜占庭验证者的行为加速两个冲突分支的最终确定的场景,以及拜占庭验证者的投票权超过三分之一关键安全阈值的情况。此外,我们重新审视了概率反弹攻击,说明了消极惩罚如何导致概率安全漏洞,可能允许拜占庭验证者超过三分之一的安全阈值。我们的研究结果揭示了惩罚不活跃节点如何损害区块链属性,特别是在存在能够协调行动的拜占庭验证者的情况下。
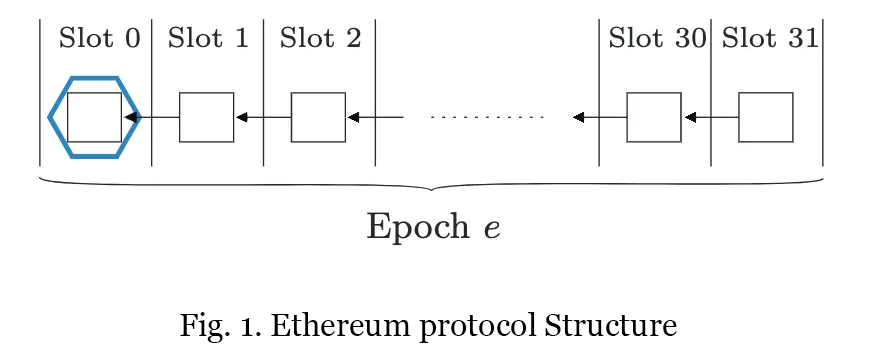
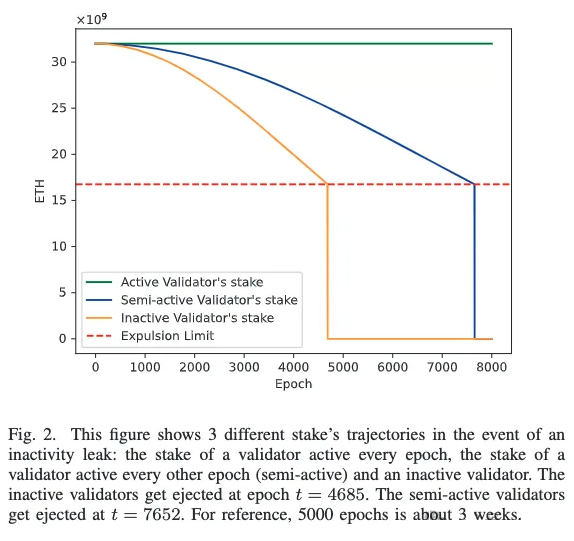
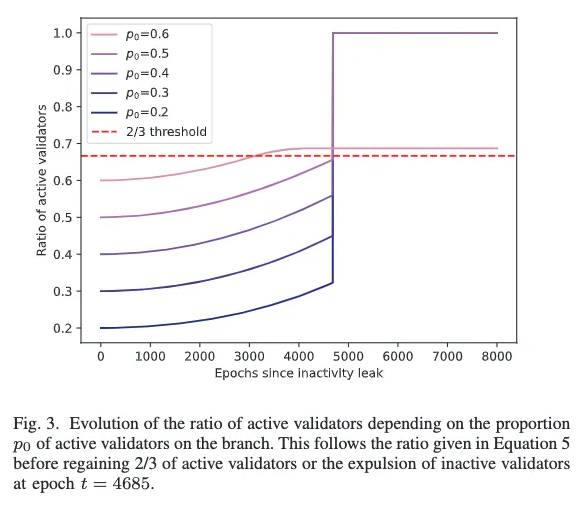
以太坊 PoS 区块链致力于实现持续增长和安全性。为了实现这些目标,协议通过激励验证者积极完成区块,并对未能完成的验证者进行惩罚。V. Buterin 和 V. Griffith 在其论文“Casper the Friendly Finality Gadget”中引入了不活跃泄漏机制,以重新获得最终性。具体来说,如果一条链连续四个时期未能完成最终确定,不活跃泄漏惩罚将启动。在不活跃泄漏期间,不活跃验证者的权益将被消耗,直到活跃验证者的权益达到总权益的三分之二。验证者未能发送证明或发送错误的目标检查点时,会在特定时期被标记为不活跃。
在不活跃泄漏期间,不再向验证者提供奖励(唯一剩下的奖励是区块生产者和同步委员会),并对不活跃验证者施加额外惩罚。不活动分数是一个动态变量,会根据验证者的活动进行调整。


验证者可分为三类:
-
- 活跃验证者:始终处于活跃状态。
-
- 半活跃验证者:每两个时期活跃一次。
-
- 不活跃验证者:始终处于不活跃状态。
被视为不活跃的验证者将受到处罚,确保以太坊 PoS 区块链的安全性和最终性。

Pdf link:https://dsn2024uq.github.io/Proceedings/pdfs/DSN2024-6rvE3SSpzFYmysif75Dkid/410500a053/410500a053.pdf
2、Profitable Arbitrage in Optimistic Rollup with ERC-721 Token Transactions
利用 ERC-721 代币交易在 Optimistic Rollup 中实现套利

Blockchain, optimistic rollups, profitable arbitrage, mempool, non-fungible tokens
区块链、乐观rollups、有利可图的套利、内存池、非同质化代币
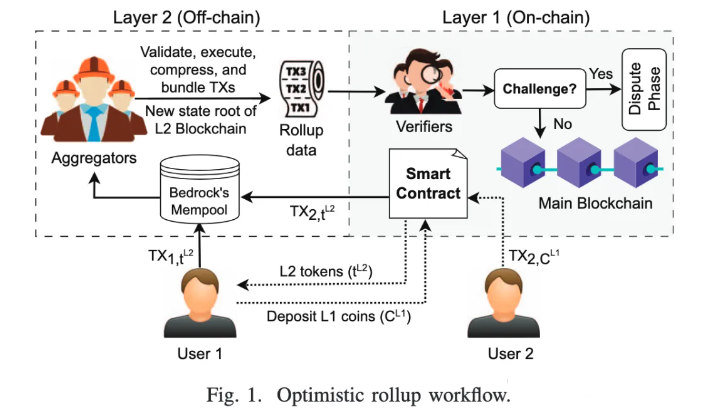
Optimistic rollup has emerged as a promising Layer 2 (L2) scaling solution for blockchain; however, its existing protocols are vulnerable to front-running and back-running activities, where an opportunistic rollup operator can strategically alter the transactions’ order to create arbitrage opportunities. Specifically, in the limited edition ERC-721 standardized non-fungible tokens (NFTs), the re-ordering of transactions introduces a lucrative threat landscape due to scarcity-driven pricing and market volatility. In this work, we introduce PAROLE, a novel attack technique on optimistic rollup systems, where an adversarial aggregator re-orders NFT transactions in an optimal way, leveraging model-free deep reinforcement learning (DRL) to maximize the balance of a target account. We created our own NFT called the “PAROLE Token” (PT) and deployed it on the OpenSea marketplace via Optimism Goerli to validate the attack impact. Furthermore, we collected NFT snapshots from rollup mainchains to analyze the impact on real-world NFT marketplaces.
Optimistic Rollup 已成为区块链的一种有前途的 Layer 2 (L2) 扩展解决方案;然而,其现有协议容易受到前端/后端交易活动的攻击,投机取巧的 Rollup 运营商可以策略性地更改交易顺序以创造套利机会。具体来说,在限量版 ERC-721 标准化非同质化代币 (NFT) 中,由于其稀缺性驱动的定价和市场波动,交易的重新排序带来了有利可图的威胁环境。在这项工作中,我们引入了 PAROLE,一种针对 Optimistic Rollup 系统的新型攻击技术,其中对抗性聚合器以最佳方式重新排序 NFT 交易,利用无模型深度强化学习 (DRL) 来最大化目标账户的余额。我们创建了自己的 NFT,称为“PAROLE 代币”(PT),并通过 Optimism Goerli 将其部署在 OpenSea 市场中以验证攻击影响。此外,我们还从汇总主链收集 NFT 快照,以分析其对现实世界 NFT 市场的影响。
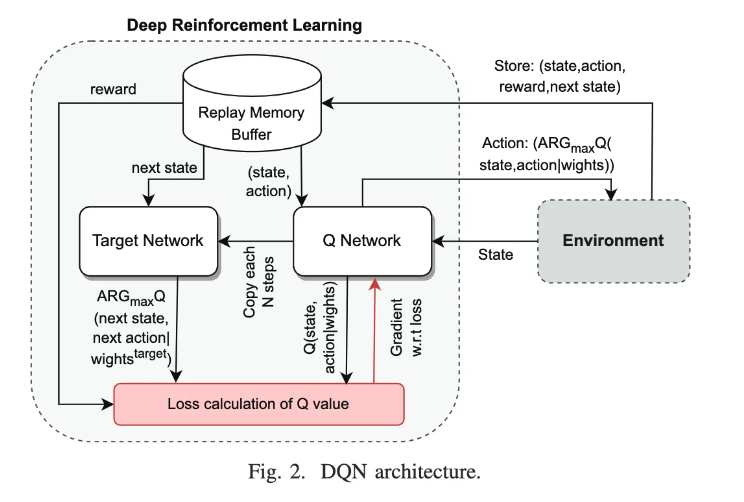
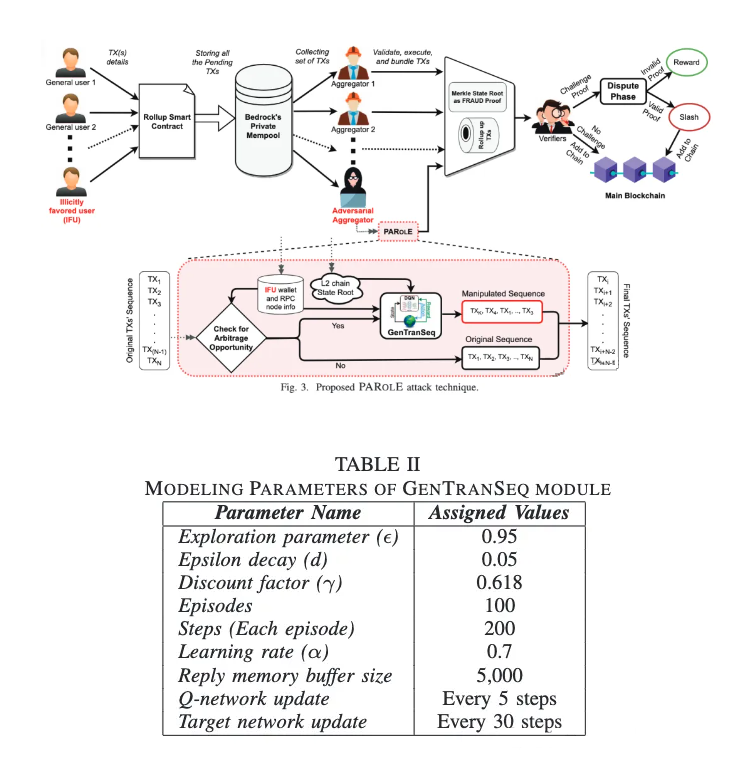
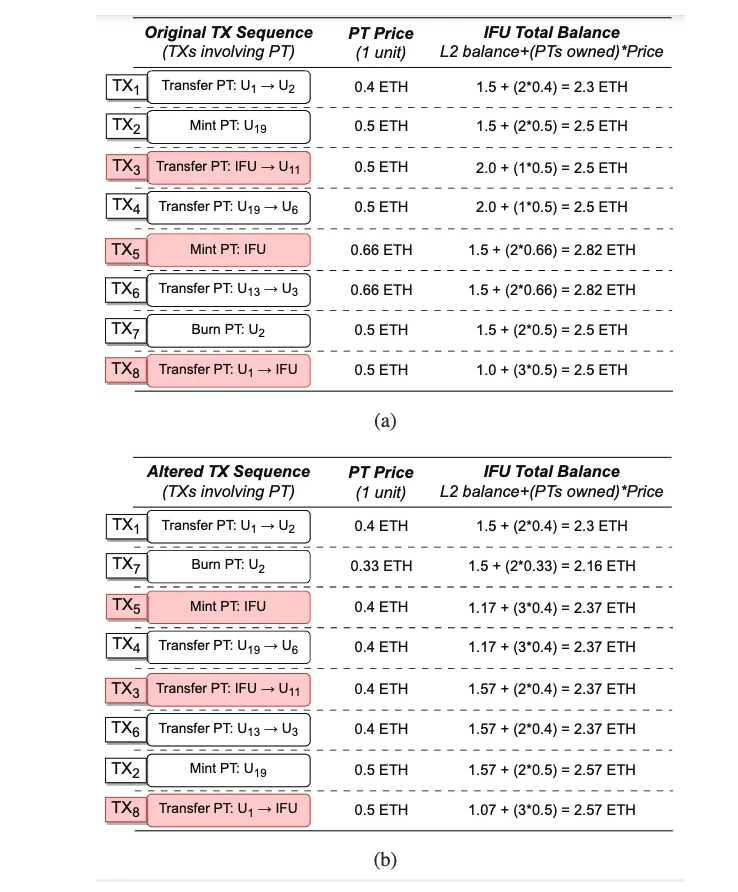
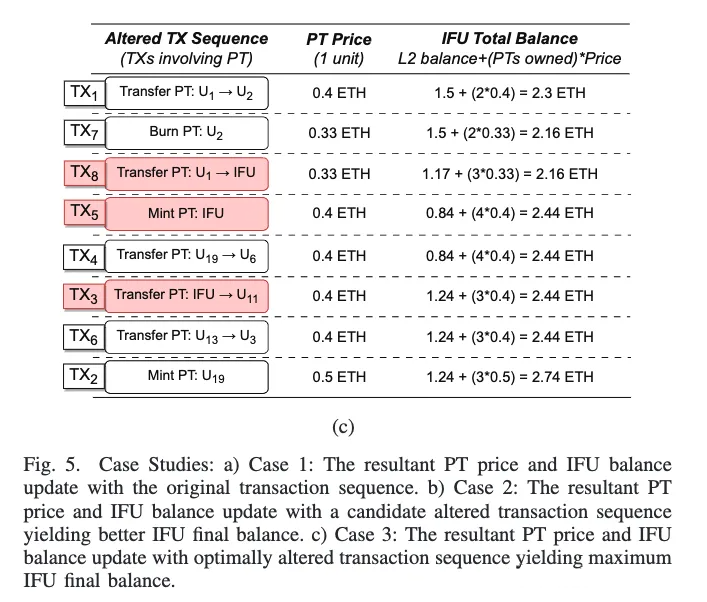
Pdf link:https://dsn2024uq.github.io/Proceedings/pdfs/DSN2024-6rvE3SSpzFYmysif75Dkid/410500a129/410500a129.pdf
3、A Blockchain to Tolerate Colluding Majorities
容忍多数人串通的区块链

Byzantine, State Machine Replication
拜占庭,状态机复制
In traditional settings, achieving consensus becomes impossible if an adversary controls one-third of the system. However, blockchain participants often reach eventual consensus despite adversaries controlling a minority of the system. This is achieved by tolerating temporary disagreements, where different participants may select different blocks for the same index before eventually agreeing on the same block. Until now, no blockchain could withstand an attacker controlling a majority of the system. In this paper, we introduce Zero-Loss Blockchain (ZLB), the first blockchain capable of tolerating an adversary controlling more than half of the system. ZLB is an open blockchain that integrates recent advances in accountable Byzantine agreement to exclude undeniably deceitful replicas, gradually reducing their proportion below one-third, and ultimately reaching consensus. Geo-distributed experiments demonstrate that ZLB outperforms HotStuff and is nearly as fast as the scalable Red Belly Blockchain, which cannot tolerate n/3 faults.
在传统环境中,如果对手控制了系统的三分之一,共识就无法实现。然而,尽管对手控制了系统的少数部分,区块链参与者通常仍能“最终”达成共识。这是通过容忍临时的分歧实现的,即不同参与者可能会为同一索引选择不同的区块,最终达成一致。到目前为止,还没有区块链能够承受控制大多数系统的攻击者。在本文中,我们介绍了零损失区块链(ZLB),这是第一个能够容忍对手控制超过一半系统的区块链。ZLB 是一个开放的区块链,它结合了可追责拜占庭协议的最新进展,以排除无可否认的欺骗性副本,逐渐将其比例减少到三分之一以下,并最终达成共识。地理分布式实验表明,ZLB 的性能优于 HotStuff,并且几乎与无法容忍 n/3 故障的可扩展 Red Belly 区块链一样快。
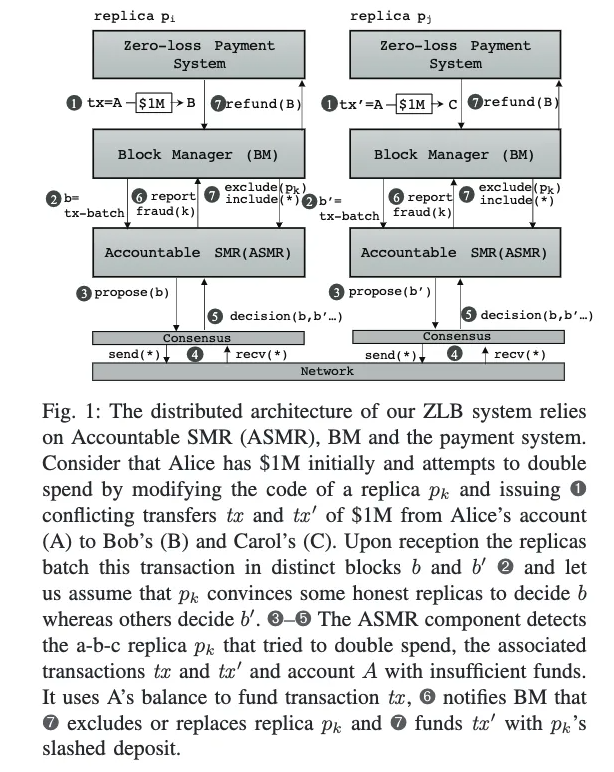
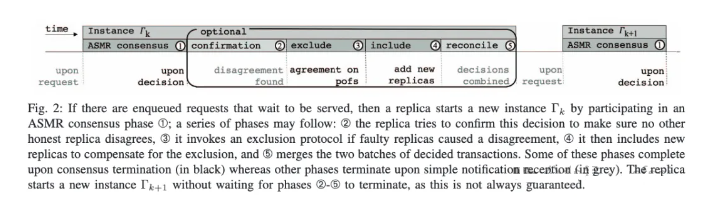

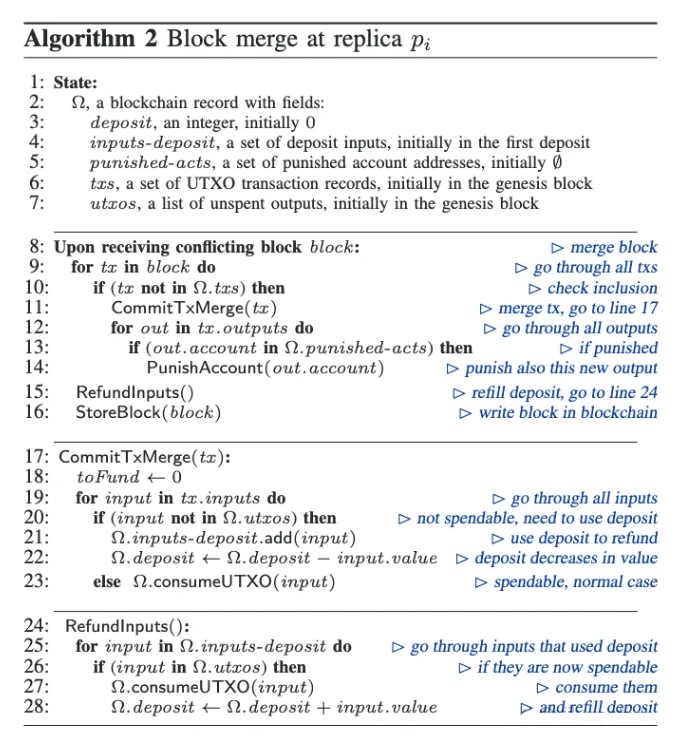
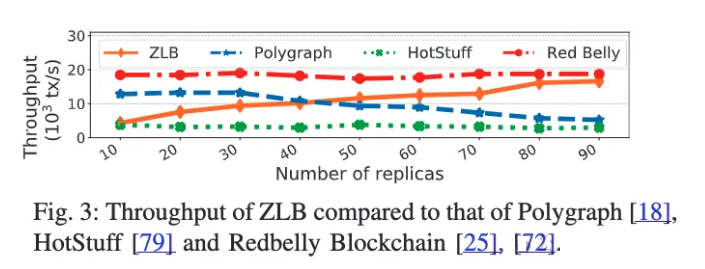
Pdf link:https://dsn2024uq.github.io/Proceedings/pdfs/DSN2024-6rvE3SSpzFYmysif75Dkid/410500a209/410500a209.pdf
4、Achieving Optimal and Fair Ordering of Financial Transactions
实现金融交易的最优和公平排序

order-fairness, asynchronous atomic broadcast, optimal communication complexity, MEV
顺序公平性、异步原子广播、最优通信复杂度、MEV
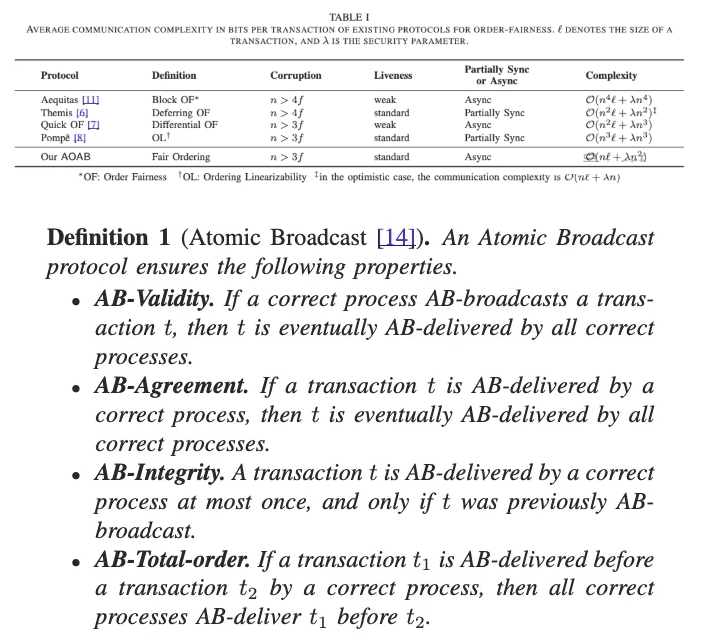
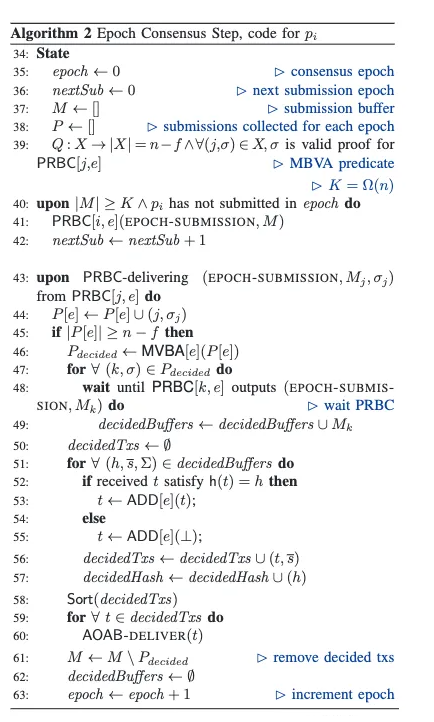
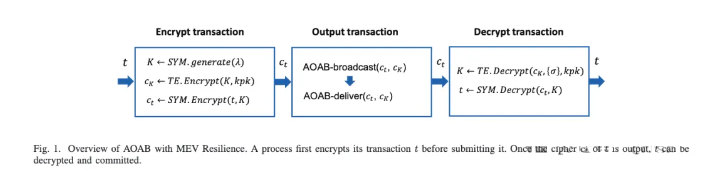
In recent years, opportunistic traders have extracted hundreds of millions of dollars from blockchains by reordering financial transactions. The problem arises because blockchains implement state machine replication that orders transactions in any consistent manner, regardless of the order in which they are received. Existing approaches to enforce the order perceived by honest participants suffer from cyclic dependencies or message delays. In this paper, we propose the Asynchronous Ordered Atomic Broadcast (AOAB) protocol. AOAB addresses these issues by (i) assigning an absolute timestamp to transactions, and (ii) tolerating unbounded message delays. Not only is AOAB the first protocol to effectively solve this problem, but it is also communication-optimal and resilience-optimal. Specifically, AOAB employs threshold signatures and information dissemination to achieve a communication complexity of O(nℓ + λn²), where n is the number of processes, ℓ is the input (transaction) size, and λ is the security parameter. This complexity is optimal when ℓ ≥ λn.
近年来,投机交易者通过重新排序金融交易从区块链中攫取了数亿美元。问题在于区块链实现的状态机复制,无论这些交易的接收顺序如何,都会以任何一致的顺序对交易进行排序。现有的强制诚实参与者感知顺序的方法存在周期性依赖或消息延迟的问题。在本文中,我们提出了异步有序原子广播(AOAB)协议。AOAB 通过以下方法解决了这些问题:(i) 为交易分配绝对时间戳,并且 (ii) 容忍无限的消息延迟。AOAB 不仅是第一个有效解决此问题的协议,还是通信最佳和弹性最佳的协议。具体而言,AOAB 利用阈值签名和信息传播,达到 O(nℓ + λn²) 的通信复杂度,其中 n 是进程数,ℓ 是输入(交易)大小,λ 是安全参数。当 ℓ ≥ λn 时,这是最佳的。

Pdf link:https://dsn2024uq.github.io/Proceedings/pdfs/DSN2024-6rvE3SSpzFYmysif75Dkid/410500a377/410500a377.pdf
文章来源:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/mJG8MQCzKMbnxFElXaILbA
